Saturday, January 21, 2012
15. A fear of phermones article
A Fear of Phermones is an article about how human's phermones affect people. Although some may think that only animals are able to secrete and smell phermones, humans can also do the same thing. Phermones are made up of several carbon atoms that animals use to distinguish the opposite sex and how to communicate with them. Animals, as well as humans, use phermones as a way to attract the opposite sex. In A Fear of Phermones, the author discussed how primates react to the different chemicals that the famales secrete. They release a phermone called estradiol that is used to attract males. My friends have recently told me how they are learning about phermones in class and one of my best girl friends just got her period. Which led another girl to another one of my bestfriends to get her period. Since we spent so much time together, I got my period the next day too. I believe what the author said was pretty accurate and that phermones do affect humans, as well as animals.
14. Lit Circle - what has surprised me the most so far
In the Beak of the Finch, the thing that surprised me the most was how one species of finch birds were able to divide into two species. Some of the birds were separated by the island for a long period of time and the two separate groups of birds had to adapt to different environments. This caused them to change and evolve into different species. But decades ago, they were the same bird. That was really interesting to me.
17. Major Plant Division
Green Algae
The green algae are the large group of algae where the higher plants emerged from. The green algae include unicellular and colonial flagellates. There are a large number of algae which sums up to be about 6,000 species of green algae. Many of the algae species live their lives as single cells, while other algae species form colonies, coenobia, long filaments, or highly differentiated macroscopic seaweeds.
Vascular Plants
These are plants that have lignified tissues used for conducting water, minerals, and photosynthetic products through the plant. Vascular plants include the club mosses, ferns, gymnosperms, and angiosperms.
Nonvascular Plants
These are plants without a vascular system. They do not have xylem or phloem. Even though these nonvascular plants don't have these particular tissues, they still have tissues that are used for internal transport of water, minerals, and other photosynthesis products.
Resources:
http://www.google.com/imgres?um=1&hl=en&client=firefox-a&sa=N&rls=org.mozilla:en-US:official&biw=1366&bih=575&tbm=isch&tbnid=svh_F_FFCTo0kM:&imgrefurl=http://www.digitalnaturalhistory.com/flora.htm&docid=WAo8we4i56NsSM&imgurl=http://www.digitalnaturalhistory.com/diapensia.jpg&w=575&h=431&ei=2OgaT_nlNqiPigLz_JDZCA&zoom=1&iact=hc&vpx=181&vpy=262&dur=318&hovh=194&hovw=259&tx=132&ty=90&sig=114823444161963020132&page=1&tbnh=159&tbnw=180&start=0&ndsp=14&ved=1t:429,r:7,s:0
http://www.google.com/imgres?um=1&hl=en&client=firefox-a&sa=N&rls=org.mozilla:en-US:official&biw=1366&bih=575&tbm=isch&tbnid=ub843ha5RuLQOM:&imgrefurl=http://www-th.bo.infn.it/tunguska/99-bryophyta.htm&docid=WZLFST3UNr-WsM&imgurl=http://www-th.bo.infn.it/tunguska/99-bryophyta.jpg&w=720&h=540&ei=BekaT5K8NunKiQLH4ZWMAw&zoom=1&iact=hc&vpx=844&vpy=358&dur=1226&hovh=139&hovw=186&tx=72&ty=80&sig=114823444161963020132&page=2&tbnh=124&tbnw=156&start=10&ndsp=27&ved=1t:429,r:4,s:10
http://www.google.com/imgres?um=1&hl=en&client=firefox-a&sa=N&rls=org.mozilla:en-US:official&biw=1366&bih=575&tbm=isch&tbnid=QFT4ZmzsH9jKBM:&imgrefurl=http://doralbio8.wikispaces.com/Red,%2BBrown%2B%2526%2BGreen%2BAlgae&docid=xvqSY4RgnCRN3M&imgurl=http://doralbio8.wikispaces.com/file/view/3329_greenAlgae_lg.jpg/205427190/3329_greenAlgae_lg.jpg&w=277&h=344&ei=FegaT__XOcWOiAKPs-nhCA&zoom=1&iact=hc&vpx=912&vpy=171&dur=87&hovh=250&hovw=201&tx=99&ty=149&sig=114823444161963020132&page=1&tbnh=162&tbnw=138&start=0&ndsp=10&ved=1t:429,r:3,s:0
The green algae are the large group of algae where the higher plants emerged from. The green algae include unicellular and colonial flagellates. There are a large number of algae which sums up to be about 6,000 species of green algae. Many of the algae species live their lives as single cells, while other algae species form colonies, coenobia, long filaments, or highly differentiated macroscopic seaweeds.
Vascular Plants
These are plants that have lignified tissues used for conducting water, minerals, and photosynthetic products through the plant. Vascular plants include the club mosses, ferns, gymnosperms, and angiosperms.
Nonvascular Plants
These are plants without a vascular system. They do not have xylem or phloem. Even though these nonvascular plants don't have these particular tissues, they still have tissues that are used for internal transport of water, minerals, and other photosynthesis products.
Resources:
http://www.google.com/imgres?um=1&hl=en&client=firefox-a&sa=N&rls=org.mozilla:en-US:official&biw=1366&bih=575&tbm=isch&tbnid=svh_F_FFCTo0kM:&imgrefurl=http://www.digitalnaturalhistory.com/flora.htm&docid=WAo8we4i56NsSM&imgurl=http://www.digitalnaturalhistory.com/diapensia.jpg&w=575&h=431&ei=2OgaT_nlNqiPigLz_JDZCA&zoom=1&iact=hc&vpx=181&vpy=262&dur=318&hovh=194&hovw=259&tx=132&ty=90&sig=114823444161963020132&page=1&tbnh=159&tbnw=180&start=0&ndsp=14&ved=1t:429,r:7,s:0
http://www.google.com/imgres?um=1&hl=en&client=firefox-a&sa=N&rls=org.mozilla:en-US:official&biw=1366&bih=575&tbm=isch&tbnid=ub843ha5RuLQOM:&imgrefurl=http://www-th.bo.infn.it/tunguska/99-bryophyta.htm&docid=WZLFST3UNr-WsM&imgurl=http://www-th.bo.infn.it/tunguska/99-bryophyta.jpg&w=720&h=540&ei=BekaT5K8NunKiQLH4ZWMAw&zoom=1&iact=hc&vpx=844&vpy=358&dur=1226&hovh=139&hovw=186&tx=72&ty=80&sig=114823444161963020132&page=2&tbnh=124&tbnw=156&start=10&ndsp=27&ved=1t:429,r:4,s:10
http://www.google.com/imgres?um=1&hl=en&client=firefox-a&sa=N&rls=org.mozilla:en-US:official&biw=1366&bih=575&tbm=isch&tbnid=QFT4ZmzsH9jKBM:&imgrefurl=http://doralbio8.wikispaces.com/Red,%2BBrown%2B%2526%2BGreen%2BAlgae&docid=xvqSY4RgnCRN3M&imgurl=http://doralbio8.wikispaces.com/file/view/3329_greenAlgae_lg.jpg/205427190/3329_greenAlgae_lg.jpg&w=277&h=344&ei=FegaT__XOcWOiAKPs-nhCA&zoom=1&iact=hc&vpx=912&vpy=171&dur=87&hovh=250&hovw=201&tx=99&ty=149&sig=114823444161963020132&page=1&tbnh=162&tbnw=138&start=0&ndsp=10&ved=1t:429,r:3,s:0
18. three key ideas; Beak of the Finch
1. natural selection - The finches on the island change and adapt to their environment. They also follow Darwin's survival of the fittest where the finch who is the most adaptable to the new environment survive and reproduce while those who lack features needed for their survival slowly die away.
2. separation - When the finches at the Galapagos island are separated from the finches elsewhere in the world, they adapt to that environment and change into a whole new version of the finch. Different finches living in different areas of the world adapt to their environment. When they adapt to it, the pass it on to their offsprings and after several generation, a noticeable difference will show in the two sets of birds.
3. adaptation - This tied in with the previous two key ideas. Adaptation is vital to the survival of the finches, they had no where else to go but the island. Being isolated from the society, they must learn how to adapt to survive or die. Some of the finches adapted to eating fruits for survival which changed their beak size to a larger beak so it's easier to break open fruits and eat them. Some of the finches adapted to eating bugs so they had a narrower, longer beak to be able to capture the critters with ease. Their beaks were one of the main adaptations they made after separation and natural selection hence the name of the book Beak of the Finch.
2. separation - When the finches at the Galapagos island are separated from the finches elsewhere in the world, they adapt to that environment and change into a whole new version of the finch. Different finches living in different areas of the world adapt to their environment. When they adapt to it, the pass it on to their offsprings and after several generation, a noticeable difference will show in the two sets of birds.
3. adaptation - This tied in with the previous two key ideas. Adaptation is vital to the survival of the finches, they had no where else to go but the island. Being isolated from the society, they must learn how to adapt to survive or die. Some of the finches adapted to eating fruits for survival which changed their beak size to a larger beak so it's easier to break open fruits and eat them. Some of the finches adapted to eating bugs so they had a narrower, longer beak to be able to capture the critters with ease. Their beaks were one of the main adaptations they made after separation and natural selection hence the name of the book Beak of the Finch.
Saturday, January 14, 2012
13. cell poem
Cells are small, but many
You can't live if you don't have any.
Cells are able to live on their own,
they are the smallest living thing,
But when they come together,
they can even make up a king.
Cells have many organelles,
including a nucleus with many orders to tell.
The membrane around the cell is all about
controlling what comes in and out.
You can't live if you don't have any.
Cells are able to live on their own,
they are the smallest living thing,
But when they come together,
they can even make up a king.
Cells have many organelles,
including a nucleus with many orders to tell.
The membrane around the cell is all about
controlling what comes in and out.
12. diversity of cells wordle
Cells are diverse in many ways including their size and functions. In cell sizes, they can range from as little as 1 micrometer to as big as 200 micrometers. One advantage of being small is the large surface to volume ratio. This ratio is important because it helps things to be moved in and out of the cell efficiently and quickly. In addition, the diffusion time to the center of the cell is a lot lower than if the cell was larger. Some cells die when they are mature in example: xylem cells. Different cells serves different purposes including red blood cells, nerve cells, rod cells, phloem cells and xylem cells.
11. Cellular Metabolim Wordle
Cellular metabolism differ depending if it's a plant or an animal. But whether it's an animal or a plant, cellular serves ones main purpose which is to produce ATP. Cells have many, many different activities to carry out in order to maintain their proper functions. These chemical reactions all need energy. Through their metabolic systems, they produce energy which is used to carry out the various activities. Plant cells use photosynthesis while animal cells use aerobic respiration.
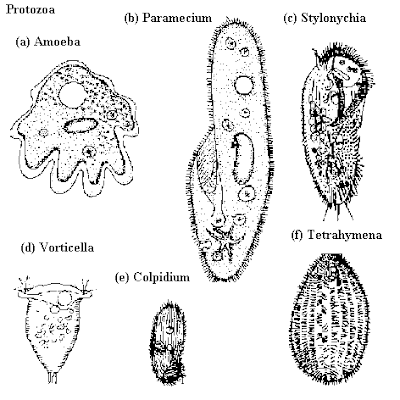
10. phyla protozoa
a.) amoeba - cell's organelles and cytoplasm are enclosed by a cell membrane
-obtains food through phagocytosis
-heterotrophs
-single large tubular pseudopod at the anterior end
-several secondary tubular pseudopods on the sides
-about 220-740μm in length
-have at least one nuclei
-food is digested in vacuoles
-asexual
b.) paramecium - slipper shaped
-about 70 - 140 um
-covered with simple cilia
-moves about 12 body lengths per second
-heterotrophs
c.) stylonychia - has cilia grouped into membranelles along the mouth
-has cirri over the body
-long cirri at the posterior (about 3)
-carnivrous
d.)vorticella - inverted bell shape
-they are anchored onto the substrate
-live in freshwater ponds
-reproduce by budding
e. colpidium - curves left
-twist forward parallel to anterior
-swims in a spiral, rotating around their long axis
-kidney shaped
-found in moist soil
f.) tetrahymena - have two types of cell nuclei ( large and small)
-have hundreds of cilia
-complicated microbule structures
-switch from commensalistic to pathogenic modes of survival
-easy to cultivate and study
9. bacteria, virus, prion, protist
Bacteria are single cell organisms, with countless varieties that have different effect on the organisms. They have a wide range of shapes including spheres, rods, and spirals. These organisms can be found almost anywhere on Earth, from the skin on our body to the hair on our head. Plants and animals also have hundreds of thousands of bacteria living within and outside of them. One gram of soil can contain up to forty million bacteria cells in it.
Unlike bacteria, viruses are small infectious agents. Bacteria are able to be spread easily while viruses can only replicate inside human beings or other living cells of organisms. Besides human beings, they are able to infect all sorts of organisms from animals to plants to bacteria.
Another infectious agent is the prion. Prion is made up of a type of protein that is folded differently than a regular protein. They are able to transmit different diseases to organisms, similar to bacteria and viruses, including mad cow disease. Unlike some bacterial and viral diseases, prion infections are deadly because all the known prion diseases target the neural tissues including the brain. These diseases have no known cure.
Protists are a group of different eukaryotic microorganisms with a variety of different unicellular organisms. They are either uniceullular or multicellular without specialized tissues which makes them a lot more simple than the other organisms. The usually live in water which could also be in the human body. Some protists are beneficial to the human body and do not harm them like viruses and prions.
Unlike bacteria, viruses are small infectious agents. Bacteria are able to be spread easily while viruses can only replicate inside human beings or other living cells of organisms. Besides human beings, they are able to infect all sorts of organisms from animals to plants to bacteria.
Another infectious agent is the prion. Prion is made up of a type of protein that is folded differently than a regular protein. They are able to transmit different diseases to organisms, similar to bacteria and viruses, including mad cow disease. Unlike some bacterial and viral diseases, prion infections are deadly because all the known prion diseases target the neural tissues including the brain. These diseases have no known cure.
Protists are a group of different eukaryotic microorganisms with a variety of different unicellular organisms. They are either uniceullular or multicellular without specialized tissues which makes them a lot more simple than the other organisms. The usually live in water which could also be in the human body. Some protists are beneficial to the human body and do not harm them like viruses and prions.
Tuesday, January 10, 2012
8. bacterial transformation and transduction video
Boyer and Cohen's goal was to get the plasmids into E. coli. Through a chemical experiment, they mixed the bacteria and the DNA in a mixture of calcium chloride. This mixture was set at a freezing temperature. They later created a "heat shock" by raising the temperature to 42 degrees Celsius and lowering the temperature back down to the freezing temperature. Through this procedure, the bacteria takes in the plasmid DNA. Later the resulting bacteria was placed in an environment with only tetracyline and kanamycin where only the transformed bacteria could thrive. This showed that the bacteria had the two genes needed for them to survive in that environment which were the tet and kan. Some resulted in doubly transformed bacteria. Through this experiment, Boyer and Cohen were able to distinguish between the different plasmids in the colony.
E. coli have adhesion zones where they have lipid molecules with negatively charged phosphates used to repel plasmid DNA. The lowered temperature decreases the movements of the lipids which in turn makes them easier to shield. When the heat shock occurs, the DNA is able to penetrate the adhesion zone.
E. coli have adhesion zones where they have lipid molecules with negatively charged phosphates used to repel plasmid DNA. The lowered temperature decreases the movements of the lipids which in turn makes them easier to shield. When the heat shock occurs, the DNA is able to penetrate the adhesion zone.
7. 3 beneficial bacteria + pictures
1. normal microbiota
These bacteria live on human skin and can also be found in the mucous membranes. They have many beneficial uses including easing the maturation of the immune system, help with digestion, fight other bad bacteria, and destry various toxins in our body. The normal microbiota is only beneficial when they are in the right place and if the human has a strong enough immune system to support them. If this bacteria was found in an area they are not usually in, the human could get sick from it, especially if it's able to penetrate it's weak immune system.
2. Lacto bacilli
This bacteria is mainly important to females because it is found in the vagina. The lacto bacilli bacteria almost immediately appear in the vagina after the baby girl is born. It takes the place of other bacteria before they could inhabit the vagina. They make that area acidic enough so that other harmful bacteria cannot penetrate it. When the baby grows up to a young lady, but before she reaches puberty, other bacteria will be taking the place of this and making it acidic. But after puberty, the lactobacilli will be able to inhabit it again.
3. Staphylococcus Epidermidis
As a member of the normal microbial flora groups, this bacteria is also vital to humans. It's found usually on the outermost layer of the human skin, if not really close to it. Sometimes, it is in the hair follicles, ready to be in action if the skin is washed. The staphylococcus Epidermidis is the first layer of defense against various bacteria and germs that human come in contact with daily. These bacteria are so small and are able to cover so much surface area at once that they make up about 10,000 to 100,000 on each square centimeter of skin.
resource used (for information)
resources for pictures:
http://www.google.com/imgres?hl=en&biw=670&bih=559&gbv=2&tbm=isch&tbnid=39e9h7Yxp01yLM:&imgrefurl=http://www.niaid.nih.gov/LabsAndResources/labs/aboutlabs/lhbp/pathogenMolecularGeneticsSection/Pages/otto.aspx&docid=dML8dWYWnLlzGM&imgurl=http://www.niaid.nih.gov/SiteCollectionImages/labs_scientific/labs/aboutlabs/lhbp/staphylococcus_epidermidis.jpg&w=300&h=390&ei=HwoNT7eDJ-ihiQLv0IjqAw&zoom=1&iact=hc&vpx=125&vpy=162&dur=366&hovh=166&hovw=150&tx=115&ty=250&sig=114823444161963020132&page=1&tbnh=166&tbnw=150&start=0&ndsp=6&ved=1t:429,r:3,s:0http://www.google.com/imgres?num=10&um=1&hl=en&client=firefox-a&hs=CoV&rls=org.mozilla:en-US:official&biw=670&bih=559&tbm=isch&tbnid=7HHrlGWhRcAmhM:&imgrefurl=http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lactobacillus&docid=pDMXRbBflOKWyM&imgurl=http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/7/7d/Lactobacillus_sp_01.png/240px-Lactobacillus_sp_01.png&w=240&h=191&ei=5AkNT9AZoqiIAtiz1Y8E&zoom=1&iact=hc&vpx=139&vpy=213&dur=1511&hovh=152&hovw=192&tx=71&ty=89&sig=114823444161963020132&sqi=2&page=1&tbnh=148&tbnw=190&start=0&ndsp=6&ved=1t:429,r:0,s:0http://www.google.com/imgres?um=1&hl=en&client=firefox-a&hs=rSq&sa=N&rls=org.mozilla:en-US:official&biw=670&bih=559&tbm=isch&tbnid=tJZko2jB_sFHNM:&imgrefurl=http://classes.midlandstech.edu/carterp/Courses/bio225/chap01/ss5.htm&docid=N_KNLh3SLJeKmM&imgurl=http://classes.midlandstech.edu/carterp/Courses/bio225/chap01/01-07_MouthMicrobio.jpg&w=719&h=603&ei=vAkNT6StG4qViALeir3xAw&zoom=1
These bacteria live on human skin and can also be found in the mucous membranes. They have many beneficial uses including easing the maturation of the immune system, help with digestion, fight other bad bacteria, and destry various toxins in our body. The normal microbiota is only beneficial when they are in the right place and if the human has a strong enough immune system to support them. If this bacteria was found in an area they are not usually in, the human could get sick from it, especially if it's able to penetrate it's weak immune system.
2. Lacto bacilli
This bacteria is mainly important to females because it is found in the vagina. The lacto bacilli bacteria almost immediately appear in the vagina after the baby girl is born. It takes the place of other bacteria before they could inhabit the vagina. They make that area acidic enough so that other harmful bacteria cannot penetrate it. When the baby grows up to a young lady, but before she reaches puberty, other bacteria will be taking the place of this and making it acidic. But after puberty, the lactobacilli will be able to inhabit it again.
3. Staphylococcus Epidermidis
As a member of the normal microbial flora groups, this bacteria is also vital to humans. It's found usually on the outermost layer of the human skin, if not really close to it. Sometimes, it is in the hair follicles, ready to be in action if the skin is washed. The staphylococcus Epidermidis is the first layer of defense against various bacteria and germs that human come in contact with daily. These bacteria are so small and are able to cover so much surface area at once that they make up about 10,000 to 100,000 on each square centimeter of skin.
resource used (for information)
resources for pictures:
http://www.google.com/imgres?hl=en&biw=670&bih=559&gbv=2&tbm=isch&tbnid=39e9h7Yxp01yLM:&imgrefurl=http://www.niaid.nih.gov/LabsAndResources/labs/aboutlabs/lhbp/pathogenMolecularGeneticsSection/Pages/otto.aspx&docid=dML8dWYWnLlzGM&imgurl=http://www.niaid.nih.gov/SiteCollectionImages/labs_scientific/labs/aboutlabs/lhbp/staphylococcus_epidermidis.jpg&w=300&h=390&ei=HwoNT7eDJ-ihiQLv0IjqAw&zoom=1&iact=hc&vpx=125&vpy=162&dur=366&hovh=166&hovw=150&tx=115&ty=250&sig=114823444161963020132&page=1&tbnh=166&tbnw=150&start=0&ndsp=6&ved=1t:429,r:3,s:0http://www.google.com/imgres?num=10&um=1&hl=en&client=firefox-a&hs=CoV&rls=org.mozilla:en-US:official&biw=670&bih=559&tbm=isch&tbnid=7HHrlGWhRcAmhM:&imgrefurl=http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lactobacillus&docid=pDMXRbBflOKWyM&imgurl=http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/7/7d/Lactobacillus_sp_01.png/240px-Lactobacillus_sp_01.png&w=240&h=191&ei=5AkNT9AZoqiIAtiz1Y8E&zoom=1&iact=hc&vpx=139&vpy=213&dur=1511&hovh=152&hovw=192&tx=71&ty=89&sig=114823444161963020132&sqi=2&page=1&tbnh=148&tbnw=190&start=0&ndsp=6&ved=1t:429,r:0,s:0http://www.google.com/imgres?um=1&hl=en&client=firefox-a&hs=rSq&sa=N&rls=org.mozilla:en-US:official&biw=670&bih=559&tbm=isch&tbnid=tJZko2jB_sFHNM:&imgrefurl=http://classes.midlandstech.edu/carterp/Courses/bio225/chap01/ss5.htm&docid=N_KNLh3SLJeKmM&imgurl=http://classes.midlandstech.edu/carterp/Courses/bio225/chap01/01-07_MouthMicrobio.jpg&w=719&h=603&ei=vAkNT6StG4qViALeir3xAw&zoom=1
Sunday, January 8, 2012
6. Extreme Organism: Hyperthermophile
There are certain organisms that thrive in environments that are too harsh for ordinary organisms to survive in. Some can live in high level of salt or water, and some can live in high levels of heat. The ones that thrives in high levels of heat are know as hyperthermophiles.These organisms usually live in an environment that's about 60 degrees Celsius or more which is about 140 degrees Fahrenheit, usually staying in a temperature of about 80 degrees Celsius. Hyperthermophiles can withstand even 100 degrees Celsius (212 degrees Fahrenheit). Along with it's addiction to heat, some of these organisms may also withstand high levels of acidity or radiation. Hyperthermophiles were first discovered by Thomas D. Brock in 1969. He found them in the Yellowstone National Park hot springs. There have been over seventy discoveries since then.
The picture above is a Metanopyrus Kandleri which can survive and thrive in an environment of about 122 degrees Celsius.
Resource Used
The picture above is a Metanopyrus Kandleri which can survive and thrive in an environment of about 122 degrees Celsius.
Resource Used
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)